In the age-old debate of cats versus dogs, one question often arises that goes beyond personality and lifestyle: how long do cats live compared to dogs? It's a query that touches the heart of every pet owner, as we all hope for as much time as possible with our beloved companions. While a definitive "number of years" can be elusive, a comprehensive look at the factors influencing the longevity of both species reveals a fascinating picture. Generally speaking, cats tend to have a longer average lifespan than dogs, but this is a generalization that needs to be explored in detail.
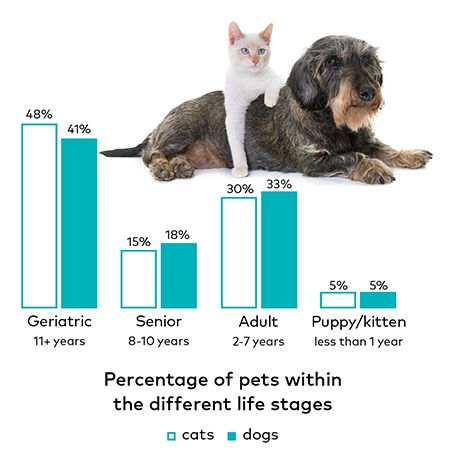
Understanding the average lifespan of cats and dogs is a good starting point. On average, a domestic cat's lifespan is between 12 and 15 years, with many living well into their late teens or even twenties. The record for the oldest cat, Crème Puff, is a staggering 38 years and 3 days. This longevity is a testament to the resilience and care that some felines receive. In contrast, the average dog's lifespan is shorter, typically ranging from 10 to 13 years. This disparity is often attributed to several key factors, which we will delve into.
One of the most significant influences on how long cats live compared to dogs is size. This is a crucial factor, especially for dogs. Smaller dog breeds, such as Chihuahuas and Yorkshire Terriers, often have a much longer lifespan, sometimes living up to 15-20 years. On the other hand, larger and giant dog breeds, like Great Danes and Bernese Mountain Dogs, have a notably shorter lifespan, often only living 6 to 10 years. The science behind this is complex, but it is believed that larger dogs age more rapidly, with their cells and bodies experiencing more wear and tear over a shorter period. This size-related longevity is less pronounced in cats, as the size difference between a Maine Coon and a Siamese is not as vast as that between a Chihuahua and a Great Dane.
Breed also plays a critical role in the lifespan of both species. Certain cat breeds are known for their longevity. For instance, Siamese and Manx cats are often reported to live longer than the average, with some reaching 20 years or more. Similarly, in the canine world, certain breeds are predisposed to longer lives. Jack Russell Terriers, for example, are known for their long lifespans. Conversely, some brachycephalic (flat-faced) breeds, like Bulldogs and Pugs, and some giant breeds are susceptible to specific health issues that can shorten their lives. Therefore, when considering the question "how long do cats live compared to dogs," it's essential to factor in the specific breed of each animal.
Another major contributor to the disparity in lifespans is health and genetics. Cats, on the whole, seem to have fewer genetic predispositions to severe health issues compared to many dog breeds. While both animals can suffer from various ailments, certain dog breeds are prone to conditions like hip dysplasia, heart disease, and specific types of cancer, which can significantly shorten their lives. Of course, cats are not immune to health problems. Feline leukemia, kidney disease, and hyperthyroidism are common issues in older cats. However, the general genetic makeup of cats seems to confer a slight longevity advantage.
Diet and nutrition are fundamental pillars of a pet's health and directly impact their lifespan. A well-balanced diet appropriate for the pet's age, size, and activity level can prevent obesity and related health problems like diabetes and joint issues. For both cats and dogs, a diet rich in high-quality proteins, healthy fats, and essential vitamins and minerals is crucial. The quality of food can make a world of difference in a pet's health trajectory.
Veterinary care is another non-negotiable factor. Regular check-ups, vaccinations, and preventative care can catch potential health problems early, allowing for timely treatment and management. This is especially true for older pets. For a cat, routine vet visits can detect early signs of kidney disease or hyperthyroidism. For a dog, they can help manage arthritis or monitor heart health. The commitment to consistent veterinary care is one of the most impactful things a pet owner can do to ensure their pet's maximum lifespan, regardless of species.
Spaying or neutering your pet is a widely recommended practice with proven health benefits that contribute to a longer life. For female cats and dogs, spaying can prevent uterine infections and tumors and significantly reduce the risk of mammary cancer. For males, neutering can prevent testicular cancer and some prostate problems. This simple procedure is a crucial part of responsible pet ownership and contributes significantly to the answer of "how long do cats live compared to dogs?" as it increases the potential for a longer, healthier life for both.
Lifestyle and environment also play a critical role in how long a cat lives versus a dog. An indoor cat, for instance, is protected from the numerous dangers of the outdoors, such as traffic, predators, diseases, and fights with other animals. An indoor-only lifestyle can add several years to a cat's lifespan. While some dogs are primarily indoor pets, many still have a significant amount of outdoor time. This exposes them to different risks, although usually not to the same degree as an outdoor cat. A dog's lifestyle also involves a lot of exercise and social interaction, which are important for their mental and physical health.
Mental stimulation and emotional well-being are just as important as physical health. Stress and anxiety can have a negative impact on a pet's health, leading to behavioral problems and even physical ailments. Providing a stimulating environment with toys, puzzles, and social interaction is crucial for both cats and dogs. A happy pet is more likely to be a healthy pet, and mental health is an often-overlooked aspect of longevity.
In conclusion, while the general answer to "how long do cats live compared to dogs?" is that cats tend to have a longer average lifespan, this is not a universal truth. The specific breed, size, genetic health, diet, veterinary care, spay/neuter status, and lifestyle all combine to determine a pet's individual longevity. A well-cared-for large-breed dog might outlive a neglected cat, and a small dog might live just as long as, or even longer than, a cat. The key takeaway for any pet owner is that the best way to ensure a long and healthy life for your furry friend is through responsible, attentive, and loving care. This includes providing a high-quality diet, regular veterinary check-ups, a safe environment, and plenty of love and attention.
We can't change the genetic blueprint of our pets, but we can significantly influence their health and well-being. By focusing on preventative care, proper nutrition, and a stimulating environment, we can help our beloved companions, whether they are feline or canine, live their best and longest lives. Ultimately, the comparison of how long cats live versus dogs isn't just about a number; it's about the quality of life we can provide and the time we get to cherish with them.
SEO Keywords:
- how long do cats live compared to dogs
- cat lifespan vs dog lifespan
- how long do cats live
- how long do dogs live
- cat longevity vs dog longevity
- average lifespan of a cat
- average lifespan of a dog
- why do cats live longer than dogs
- cat vs dog lifespan
- feline longevity
- canine longevity
- pet lifespan comparison
- how to increase cat lifespan
- how to increase dog lifespan
- indoor cat lifespan
- outdoor cat lifespan
- large dog lifespan
- small dog lifespan
- cat age vs dog age
- pet health and longevity
- extending pet life
- longest living cat
- oldest cat record
- factors affecting cat lifespan
- factors affecting dog lifespan


Post a Comment